Andrew Ng on Navigating AI Careers, DeepMind CEO on Gemini 3, and Microsoft's Agent Curriculum: The Tokenizer Edition #13
This week's most valuable AI resources
Hey there! Happy holiday season to you and yours! Some very interesting resources this week. Andrew Ng shares career guidance for AI. DeepMind CEO Demis Hassabis unpacks Gemini 3, world models, and breakthroughs from AlphaFold to fusion and elsewhere, Microsoft released a curriculum for building AI agents from foundations to production.
New here?
The Tokenizer is my resource-focused newsletter edition where I curate the best papers, videos, articles, tools, and learning resources from across the AI landscape. Consider it your weekly dose of everything you need to stay ahead in machine learning.
TL;DR
What caught my attention this week:
• 📄 Papers: GUI agents reaching production-ready performance, explainable AI video detection with grounded reasoning, and unified multimodal video generation
• 🎥 Videos: DeepMind’s CEO on the future of intelligence, game physics breakthroughs from Two Minute Papers, Anthropic on AI in education, and Bloomberg’s real-world AI deployment lessons
• 📰 Reads: Practical distributed training from single GPU to clusters, formal verification’s AI-powered future, and understanding cross-entropy loss fundamentals
• 🛠 Tools: Microsoft’s comprehensive agent learning guide and DAIR’s definitive prompt engineering resource
• 🎓 Learning: Andrew Ng’s career advice for AI practitioners looking to navigate the field strategically
Thinking about a good holiday gift for your friends or family? Grab my first book — AI for the Rest of Us — today!
Quick note: If you find the book useful, please leave a review on Amazon. It makes a world of difference. If you have a picture of the book IRL, please share it with me. I really appreciate it.
📄 5 Papers
Skyra: AI-Generated Video Detection via Grounded Artifact Reasoning
https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.15693 | GitHub
AI video detection just got explainable. Skyra identifies specific visual artifacts in AI-generated videos and uses them as grounded evidence for both detection and explanation. The model introduces ViF-CoT-4K, the first large-scale dataset of AI-generated video artifacts with fine-grained human annotations. Instead of just saying “this is fake,” Skyra points to concrete inconsistencies like shape distortions or camera motion problems. The two-stage training strategy enhances spatio-temporal artifact perception while maintaining explainability. Tested against outputs from over ten state-of-the-art generators on the new ViF-Bench benchmark, Skyra outperforms existing methods while actually showing you why it reached its conclusion.
Step-GUI Technical Report
https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.15431 | GitHub
GUI automation hit production-grade numbers. Step-GUI’s 8B model achieves 80.2% on AndroidWorld, 48.5% on OSWorld, and 62.6% on ScreenShot-Pro through a self-evolving training pipeline that converts model-generated trajectories into reliable training signals. The Calibrated Step Reward System achieves over 90% annotation accuracy at 10-100x lower cost than manual annotation. Beyond the models, they introduce GUI-MCP, the first Model Context Protocol for GUI automation with hierarchical architecture combining low-level atomic operations and high-level task delegation to local specialist models. The AndroidDaily benchmark tests authentic everyday usage with 3,146 static actions and 235 end-to-end tasks across high-frequency mobile scenarios.
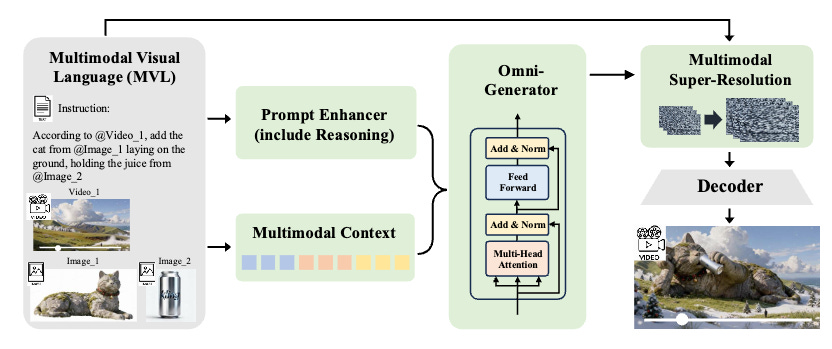
Kling-Omni Technical Report
https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.16776
Kling-Omni bridges the gap between diverse video generation tasks into a unified system. The framework handles text-to-video, image-to-video, and video editing through an end-to-end multimodal visual language approach, processing text instructions, reference images, and video contexts into a unified representation. The system delivers cinematic-quality content through efficient large-scale pre-training strategies and infrastructure optimizations. Comprehensive evaluations show exceptional in-context generation, reasoning-based editing, and multimodal instruction following capabilities, moving beyond content creation toward multimodal world simulators.
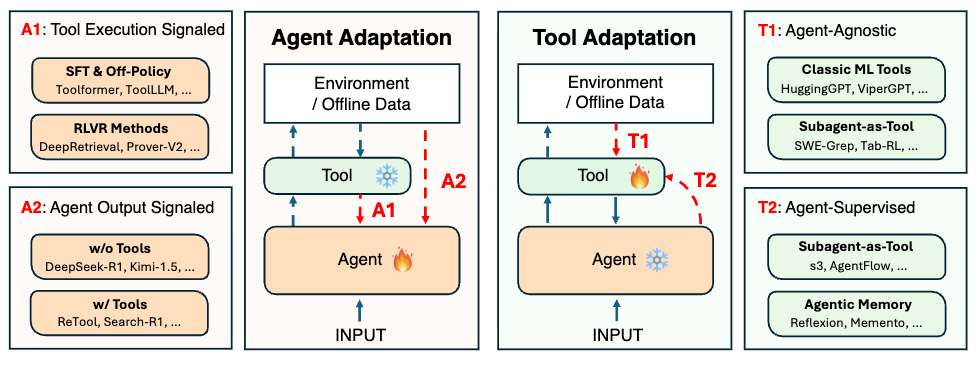
Adaptation of Agentic AI
https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.16301 | GitHub
A systematic framework for understanding adaptation in agentic AI systems. The paper unifies the expanding research landscape into agent adaptations (tool-execution-signaled and agent-output-signaled) and tool adaptations (agent-agnostic and agent-supervised). This framework clarifies the design space of adaptation strategies, makes trade-offs explicit, and provides practical guidance for selecting or switching among strategies during system design. The comprehensive survey reviews representative approaches in each category, analyzes strengths and limitations, and highlights key open challenges for building more capable and reliable agentic systems.
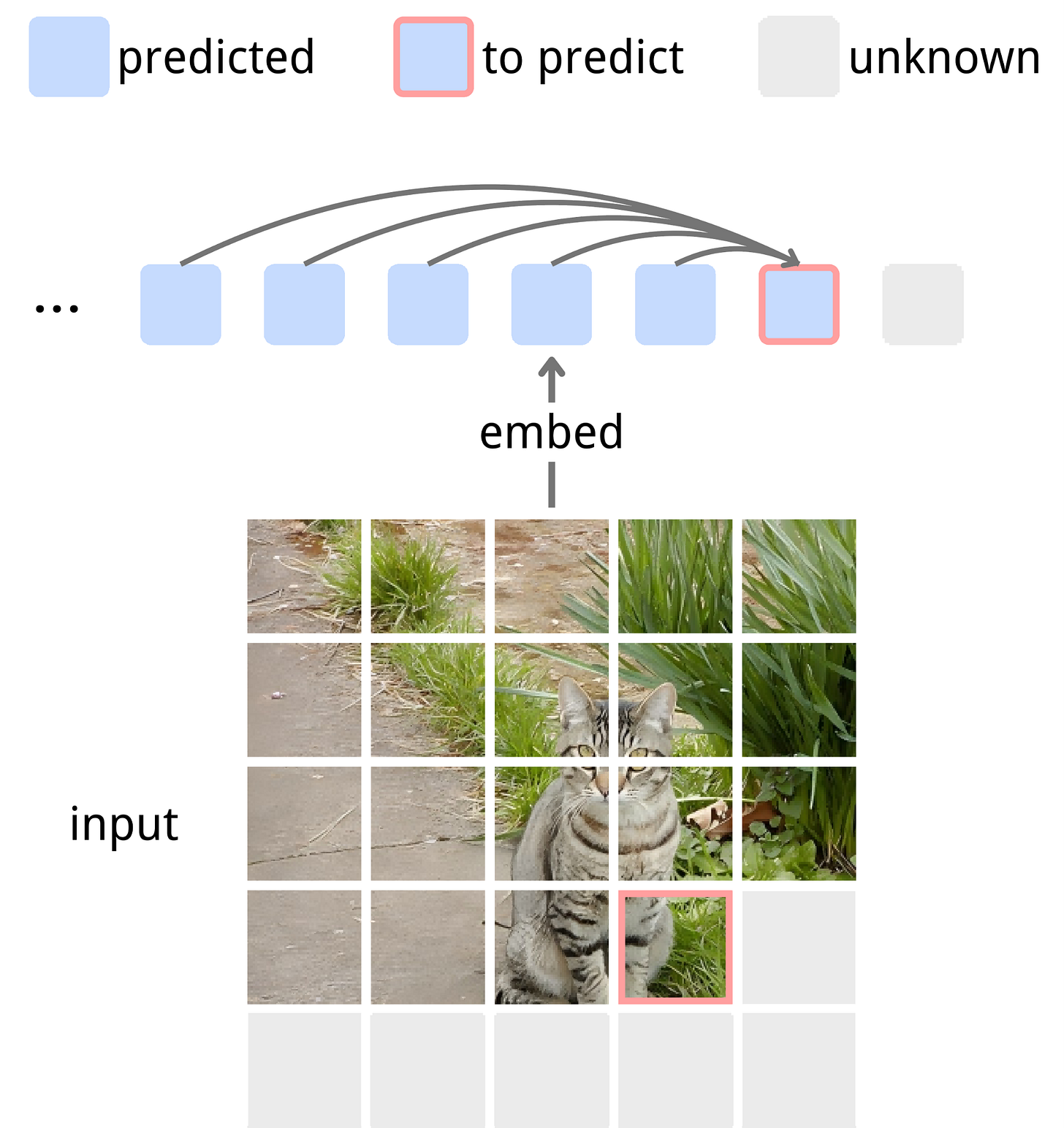
Next-Embedding Prediction Makes Strong Vision Learners
https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.16922 | GitHub
Generative pretraining comes to computer vision through next-embedding prediction. Instead of training models to output features, NEPA trains them to generate embeddings for predictive tasks directly. Models learn to predict future patch embeddings conditioned on past ones using causal masking and stop gradient. A simple Transformer pretrained on ImageNet-1k with next embedding prediction as its sole objective achieves 83.8% and 85.3% top-1 accuracy with ViT-B and ViT-L backbones after fine-tuning. No pixel reconstruction, discrete tokens, contrastive loss, or task-specific heads required. The approach transfers effectively to semantic segmentation on ADE20K, suggesting generative pretraining from embeddings provides a simpler, scalable alternative to current visual self-supervised learning.
🎥 4 Videos
The future of intelligence | Demis Hassabis (Co-founder and CEO of DeepMind)
DeepMind’s CEO discusses the current state and future directions of artificial intelligence in this 50-minute conversation. Demis Hassabis covers rapid advancements including Gemini 3 and world model development, progress on fundamental problems like AlphaFold, and ongoing efforts in material science, fusion, and quantum computing. The discussion explores AI’s paradoxical capabilities, its potential impact on mathematics, and balancing scientific research with commercial product development. Hassabis shares insights on scaling AI, addressing challenges like hallucinations, and the significance of simulated worlds for robotics and scientific discovery.
Game Physics Just Jumped A Generation
Károly Zsolnai-Fehér from Two Minute Papers covers a new “Domain Decomposition” method that enables real-time simulation of hyper-complex materials. The technique allows for the interaction of tens of thousands of vertices (think intricate cloth tearing or squishy “gummy” soft bodies) at interactive framerates. This represents a massive leap over previous standard solvers, which would struggle to render these interactions in real-time without exploding computationally. It’s a purely algorithmic breakthrough in physics simulation, achieving offline film-quality results in live environments without using AI approximations.
What does AI mean for education?
Anthropic examines AI’s implications for educational systems and learning approaches. The discussion explores how AI capabilities are reshaping traditional educational paradigms, the opportunities for personalized learning, and considerations for implementing AI in educational contexts while maintaining pedagogical principles. The video provides frameworks for educators and institutions thinking about AI integration in learning environments.
What We Learned Deploying AI within Bloomberg’s Engineering Organization
Lei Zhang from Bloomberg shares lessons from deploying AI across their engineering organization. The talk covers practical challenges of real-world AI adoption, organizational insights from implementing AI at scale, and what actually works versus what sounds good in theory. Bloomberg’s experience provides valuable perspectives on moving from AI prototypes to production systems that serve actual business needs across a large technology organization.
📰 3 Curated Reads
From Single GPU to Clusters: A Practical Journey into Distributed Training with PyTorch and Ray
https://debnsuma.github.io/my-blog/posts/distributed-training-from-scratch/
A hands-on guide to scaling deep learning from single GPU experiments to multi-node clusters. The post walks through the progression from local training to distributed setups using PyTorch and Ray, covering practical considerations for data parallelism, model parallelism, and orchestrating training across multiple machines. Particularly useful for practitioners hitting GPU memory limits or training time constraints who need to move beyond single-machine setups without getting lost in distributed systems complexity.
Prediction: AI will make formal verification go mainstream
https://martin.kleppmann.com/2025/12/08/ai-formal-verification.html
Martin Kleppmann argues that AI will finally bring formal verification into widespread use. The piece explores how large language models could lower the barrier to writing formal specifications and proofs, making techniques that were previously restricted to critical systems accessible for everyday software development. The analysis examines the current state of formal verification, why it hasn’t achieved mainstream adoption despite proven benefits, and how AI assistance could change the economics of using these tools.
Cross Entropy Loss
https://cgnarendiran.github.io/blog/cross-entropy-loss/
A clear, intuitive explanation of cross-entropy loss rooted in information theory. The post breaks down the concept of “surprise” (self-information) using a simple weather prediction analogy to explain why we penalize confident wrong answers so heavily. It walks through the mathematical connection between Entropy, Cross-Entropy, and KL Divergence, showing exactly how the loss function measures the distance between the predicted probability distribution and the actual ground truth. A great refresher for understanding the “why” behind the most common classification loss function.
🛠 2 Tools & Repos
AI Agents for Beginners
https://github.com/microsoft/ai-agents-for-beginners
Microsoft’s comprehensive introduction to building AI agents. The curriculum covers fundamental concepts, agent architectures, tool integration, and practical implementations. Designed for developers new to agentic AI, the course provides hands-on examples and clear explanations of core concepts needed to build working agents. The structured approach takes you from basic agent patterns to more sophisticated multi-agent systems.
Prompt Engineering Guide
https://github.com/dair-ai/Prompt-Engineering-Guide
DAIR.AI’s definitive resource for prompt engineering techniques. The guide covers fundamental prompting strategies, advanced techniques like chain-of-thought and tree-of-thought reasoning, domain-specific applications, and best practices for different model families. Regularly updated with the latest research and techniques, this remains one of the most comprehensive and well-maintained prompt engineering resources available.
🎓 1 Pick of the Week
Career Advice in AI
Andrew Ng shares strategic career advice for AI practitioners. The discussion covers how to build skills that compound over time, choosing between research and engineering paths, navigating the rapidly evolving AI landscape, and positioning yourself for long-term success in the field. Ng’s perspective comes from experience building AI teams at Google Brain and Baidu, founding Coursera and DeepLearning.AI, and advising countless AI careers. Particularly valuable for anyone making career decisions in AI or trying to understand where the field is heading.
Thanks for reading The Tokenizer! If you found something useful here, share it with someone who might benefit. And if you want more curated insights like this, consider subscribing to Gradient Ascent.




always a pleasure to listen to Andrew :)