DeepSeek's Human-Like Vision, Chip Huyen's AI Tools Site, and Stanford's Updated LLM Course - 📚 The Tokenizer Edition #16
This week's most valuable AI resources
Hey there! DeepSeek just redefined how vision models process documents by teaching them to read with human-like logic instead of rigid top-to-bottom scanning. Meanwhile, Ant Group released a world simulator achieving minute-long consistent video generation with sub-second interaction latency. Open-source continues delivering production-ready systems.
New here?
The Tokenizer is my resource-focused newsletter edition where I curate the best papers, videos, articles, tools, and learning resources from across the AI landscape. Consider it your weekly dose of everything you need to stay ahead in machine learning.
I’m teaching ML & Generative AI System Design on Feb 28th / March 1st with Packt.
Gradient Ascent Special: Use code FLASH40 for 40% off
We’ll cover the core system design principles for building solid AI products: making systems reliable, measuring what matters, and designing architectures that work in production.
Through live discussions, guided exercises, and team-based design sprints, you’ll practice solving system-level AI problems and walk away with frameworks you can apply immediately at work.
What topics/problems would you most want covered in a system design workshop? Drop a comment or DM me.
TL;DR
What caught my attention this week:
📄 Papers: Vision encoders with causal reasoning for document understanding, open-source world simulators rivaling closed systems, plus advances in mathematical reasoning and multimodal scientific models
🎥 Videos: Pydantic fundamentals for ML engineers, building agent frameworks from scratch, production AI coding workflows, and understanding diffusion versus flow matching
📰 Reads: Reinforcement learning for continual LLM adaptation, preparing for ML interviews beyond just attention mechanisms, and DeepSeek’s latest architectural innovations
🛠 Tools: Curated resources for agentic reasoning research and comprehensive AI tool directories
🎓 Learning: Stanford’s updated large language model course covering recent advances
📄 5 Papers
DeepSeek-OCR 2: Visual Causal Flow
https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.20552 | GitHub
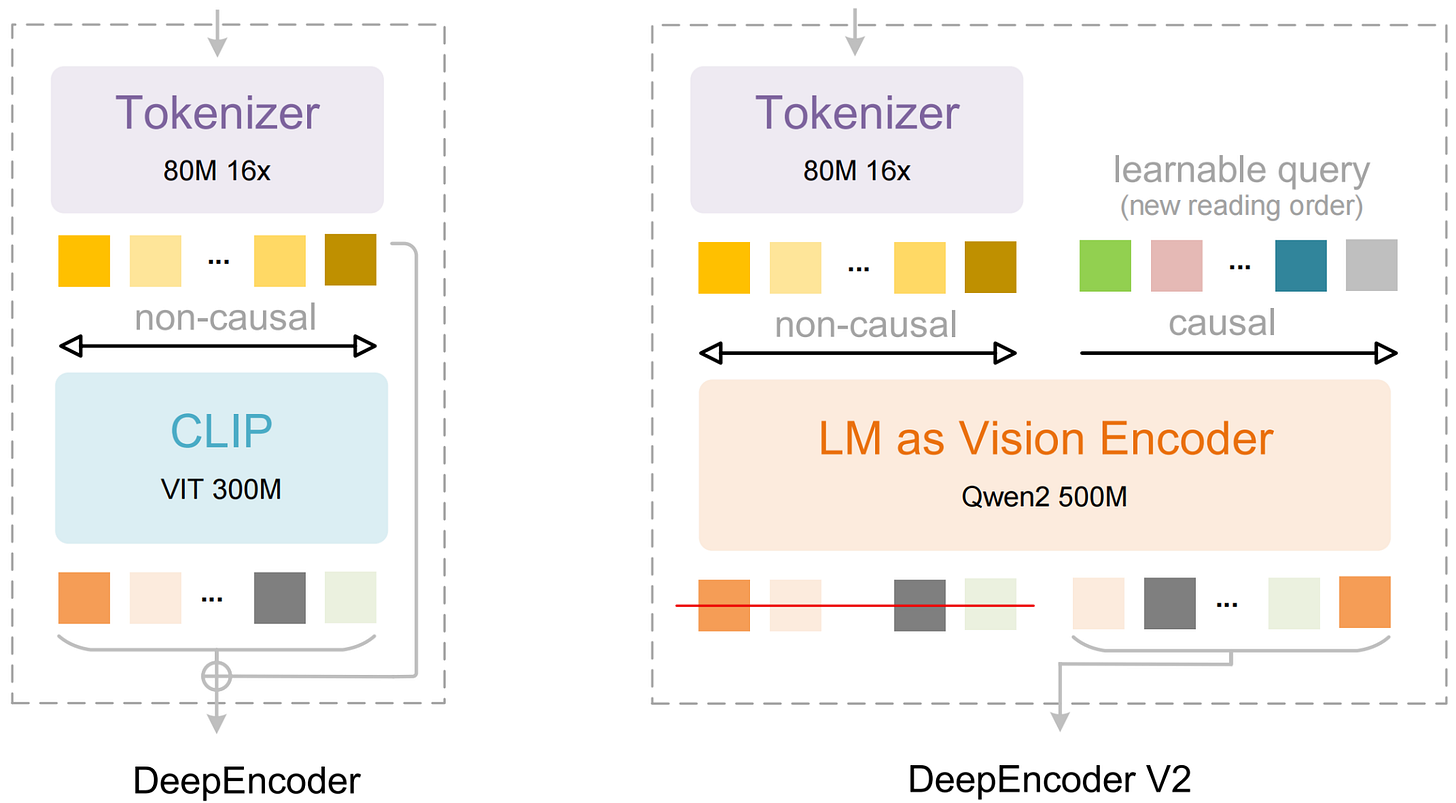
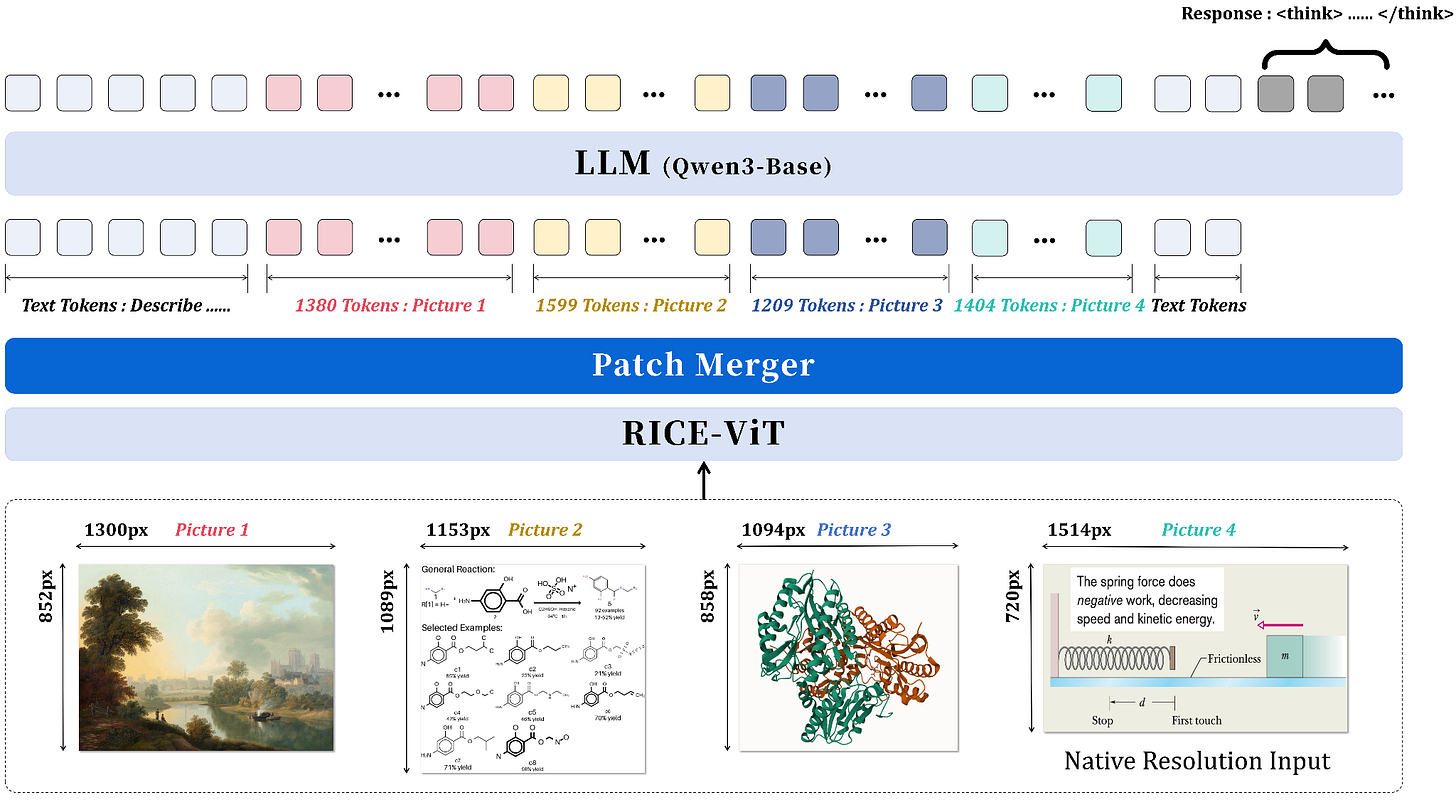
Instead of processing images in rigid raster-scan order, DeepSeek-OCR 2 introduces DeepEncoder V2 that mimics how humans actually read documents. The encoder uses causal attention to dynamically reorder visual tokens based on semantic content, determining whether to scan titles first, process tables column-by-column, or navigate multi-column layouts intelligently. By replacing CLIP with Qwen2-0.5B and implementing learnable queries with causal flow, the 3B parameter model achieves 91.09% on OmniDocBench while maintaining 256-1120 token efficiency. Reading order edit distance dropped from 0.085 to 0.057, proving the system genuinely understands logical document structure rather than just memorizing patterns.
Advancing Open-source World Models
https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.20540 | GitHub
Ant Group’s LingBot-World delivers minute-long consistent video generation at 16 FPS with under 1-second interaction latency, positioning open-source world models competitively against closed systems. The system maintains high-fidelity dynamics across photorealistic, scientific, and stylized environments through a multi-stage training pipeline combining web videos with Unreal Engine synthetic data. Users control camera perspectives and environmental conditions in real-time while the model preserves spatial consistency across 961 frames. The hybrid data engine with hierarchical captioning separates motion control from static scene generation, addressing the training data bottleneck that typically limits world model development.
Harder Is Better: Boosting Mathematical Reasoning via Difficulty-Aware GRPO and Multi-Aspect Question Reformulation
https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.20614 | GitHub
Group Relative Policy Optimization suffers from an implicit imbalance where harder questions receive smaller policy updates, limiting capability development where it matters most. MathForge addresses this through Difficulty-Aware GRPO, which balances group advantage estimation by question difficulty and prioritizes harder problems through difficulty-aware weighting. The framework’s Multi-Aspect Question Reformulation strategy systematically increases question difficulty across multiple dimensions while maintaining gold answers, creating training data that pushes model boundaries. The synergistic loop of MQR expanding the data frontier and DGPO effectively learning from augmented data produces significant improvements across mathematical reasoning benchmarks.
Innovator-VL: A Multimodal Large Language Model for Scientific Discovery
https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.19325 | GitHub
Scientific multimodal models typically require massive domain-specific pretraining, but Innovator-VL demonstrates strong performance using fewer than five million curated samples without large-scale pretraining. The fully transparent training pipeline covers data collection, cleaning, preprocessing, supervised fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning with detailed optimization recipes, enabling systematic community extension. The model maintains competitive performance on general vision benchmarks while excelling at scientific tasks, indicating that scientific alignment integrates into unified models without compromising general-purpose capabilities. Principled data selection proves more effective than indiscriminate scaling for scientific reasoning.
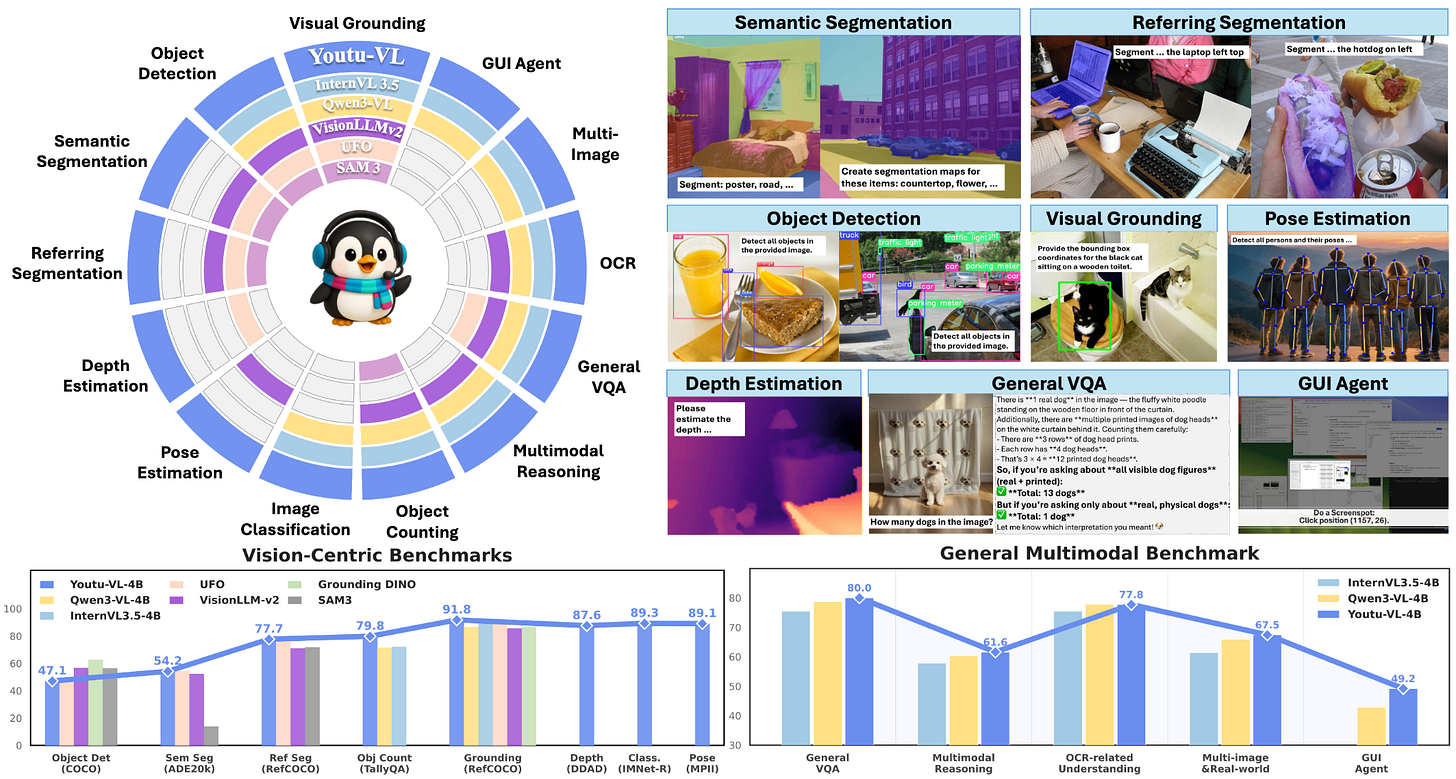
Youtu-VL: Unleashing Visual Potential via Unified Vision-Language Supervision
https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.19798 | GitHub
Vision-language models exhibit a text-dominant optimization bias by treating visual signals as passive inputs rather than supervisory targets. Youtu-VL shifts to the Vision-Language Unified Autoregressive Supervision paradigm, integrating visual tokens directly into the prediction stream and applying unified autoregressive supervision to both visual details and linguistic content. This “vision-as-target” approach fundamentally changes optimization from treating vision as conditional input to making it a prediction objective. The framework extends to vision-centric tasks without requiring task-specific architectural additions, establishing foundations for comprehensive generalist visual agents.
🎥 4 Videos
Pydantic Crash Course
Dave Ebbelaar walks through Pydantic’s data validation and settings management capabilities essential for ML engineers working with LLMs. The tutorial covers defining models with type hints, validation logic, and configuration management patterns that ensure data integrity in production AI systems. Understanding Pydantic proves critical when building structured outputs from language models or managing complex application configurations where type safety prevents runtime errors.
Building Mini ClawdBot from Scratch
Vizuara demonstrates constructing an agent like Moltbot (ClawdBot, or whatever it's called now) without relying on existing libraries, revealing the actual mechanics behind agent architectures. By building from first principles, you understand tool integration, state management, and decision-making loops that frameworks abstract away. This approach proves valuable when debugging production agent systems or architecting custom solutions that don't fit standard framework patterns.
The Senior Engineer’s Guide to AI Coding
This How I AI episode examines Claude Code workflows and architectural decisions that separate effective AI-assisted development from mere prompt engineering. It addresses code review practices, testing strategies, and integration patterns when collaborating with AI coding assistants.
Flow Matching vs Diffusion Side By Side
Letitia compares flow matching and diffusion approaches for generative modeling, clarifying when each technique provides advantages. The visual comparison helps understand why flow matching sometimes offers training efficiency benefits over traditional diffusion while maintaining generation quality. Grasping these trade-offs matters when selecting architectures for specific generative modeling tasks.
📰 3 Curated Reads
Continual Learning with RL for LLMs
Cameron Wolfe explores why Reinforcement Learning (RL) is naturally more robust than Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) for continual learning in LLMs. While traditional methods like replay buffers and regularization remain relevant, recent studies suggest that RL’s on-policy nature minimizes the distributional shifts that cause catastrophic forgetting.
Is Attention All You Need for ML Interviews?
https://medium.com/@maxwbuckley/is-attention-all-you-need-to-prepare-for-ml-interviews-830742f6d2ba
Max Buckley shares some quick tips to master the transformer architecture and its implementation ahead of ML interviews. Worth checking out to know the details of the bedrock of modern AI in case you’re preparing for interviews.
DeepSeek Drops Yet Another
Anil Ananthaswamy analyzes DeepSeek’s pattern of releasing architectural innovations that challenge conventional wisdom about model scaling and design. The examination covers their mixture-of-experts implementations, efficiency improvements, and open-source strategy that accelerates community progress. Tracking DeepSeek’s releases provides insights into architectural directions gaining traction in production systems.
🛠 2 Tools & Repos
Awesome Agentic Reasoning
https://github.com/weitianxin/Awesome-Agentic-Reasoning
This curated collection organizes research papers, codebases, and benchmarks focused on agentic reasoning capabilities in AI systems. Instead of accumulating every tangentially related work, the repository maintains editorial standards around core reasoning techniques like planning, reflection, and tool use. The structured organization helps researchers quickly locate relevant work when investigating specific reasoning approaches or comparing methodologies across different agent architectures.
GoodAI List
Chip Huyen curates AI tools and repositories with clear judgment about practical utility versus hype. The directory covers libraries, frameworks, and resources across the ML stack with emphasis on production readiness and actual adoption. Unlike comprehensive but overwhelming awesome lists, this maintains focus on tools demonstrating real-world value in AI development workflows.
🎓 1 Pick of the Week
Stanford’s LLM Course
https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLoROMvodv4rObv1FMizXqumgVVdzX4_05&si=bqJCbjmvpCx-1_51
Stanford’s curated playlist brings together lectures from multiple courses covering large language models, including CS224N (NLP with Deep Learning), CS25 (Transformers United), and CME 295 (Transformers & Large Language Models). The collection spans foundational concepts in transformer architectures and training methodologies alongside cutting-edge developments in reasoning models, multimodal systems, and efficient inference techniques.
Thanks for reading The Tokenizer! If you found something useful here, share it with someone who might benefit. And if you want more curated insights like this, consider subscribing to Gradient Ascent.