Google Dismantles Deep Learning, VLMs Ditch Text for Vision, and Karpathy Builds AI Juries: The Tokenizer Edition #10
This week's most valuable AI resources
Hey there! Google Research unveiled a paradigm that reframes deep learning as nested optimization problems rather than stacked layers. Vision-language models learned to reason in continuous visual tokens instead of forcing concepts into text. And Karpathy released a multi-model council system that has LLMs review each other’s work before producing final answers.
New here?
The Tokenizer is my resource-focused newsletter edition where I curate the best papers, videos, articles, tools, and learning resources from across the AI landscape. Consider it your weekly dose of everything you need to stay ahead in machine learning.
TL;DR
What caught my attention this week:
📄 Papers: Text-promptable medical segmentation across modalities, vision models reasoning in visual token space, humanoid agents searching 360° environments, and a provocative rethinking of deep learning architectures
🎥 Videos: Meta-optimization frameworks for AI agents, DeepMind’s scientific journey, reward hacking in production RL, and Jeff Dean on frontier AI trends
📰 Reads: Deep debugging insights from PyTorch development, practical CursorAI workflows for engineers, and understanding GRPO for reinforcement learning
🛠 Tools: Karpathy’s multi-LLM council system and Andrew Ng’s automated paper reviewer
🎓 Learning: Building Olmo 3 from scratch with Sebastian Raschka’s implementation notebook
Grab my first book — AI for the Rest of Us — today!
Quick note: If you find the book useful, please leave a review on Amazon. It makes a world of difference. If you have a picture of the book IRL, please share it with me. I really appreciate it.
📄 5 Papers
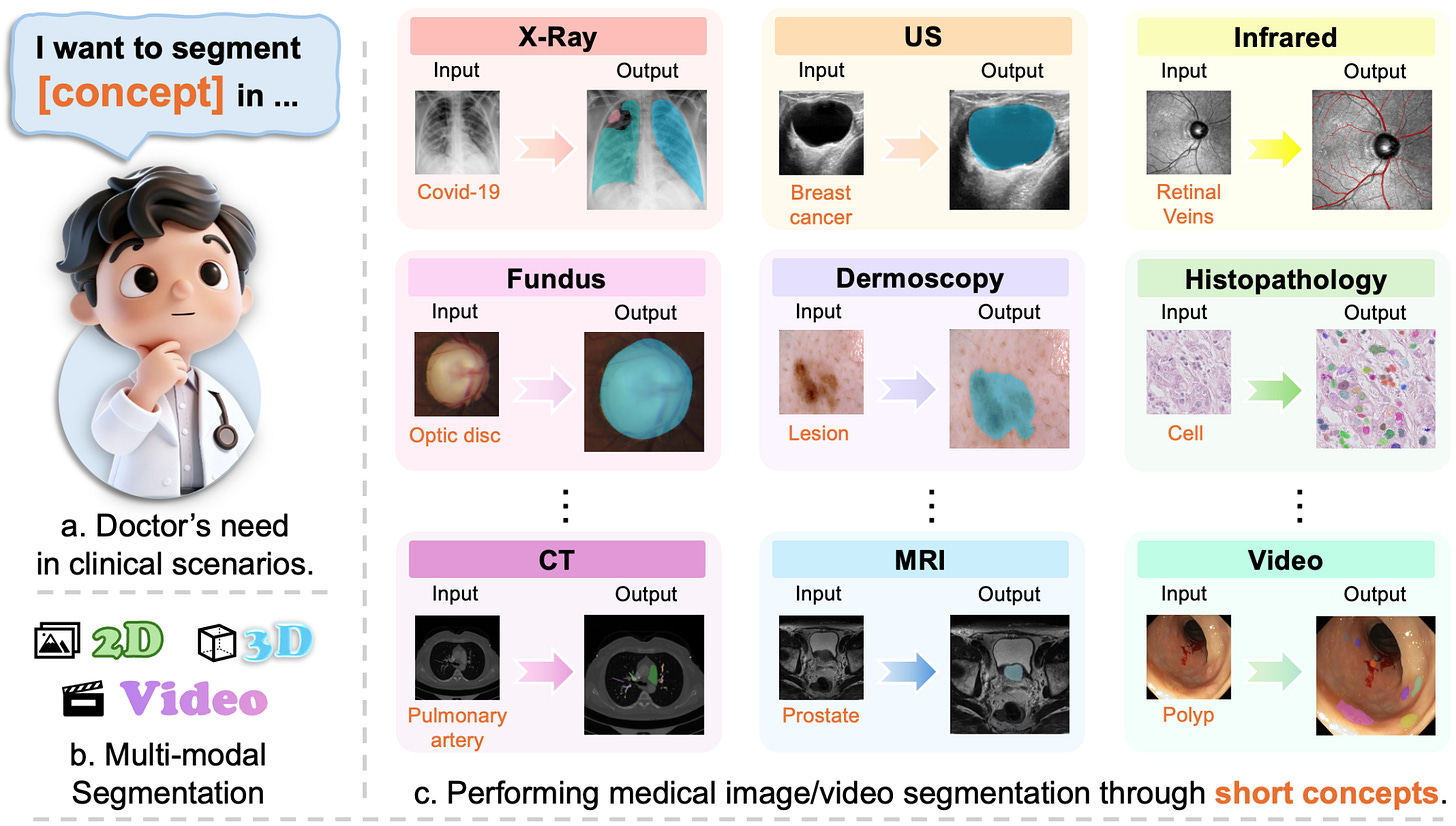
MedSAM3: Delving into Segment Anything with Medical Concepts
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.19046 | GitHub
Medical image segmentation typically demands extensive manual annotation for each new clinical application. MedSAM3 addresses this by enabling text-based prompting across diverse imaging modalities. Instead of drawing boxes or clicking points, you can segment anatomical structures using natural language like “breast tumor” or “pulmonary artery.” The system works across X-ray, MRI, Ultrasound, CT, and video by fine-tuning SAM 3 with semantic conceptual labels. The MedSAM3 Agent framework integrates multimodal LLMs for complex reasoning and iterative refinement, allowing practitioners to interact with medical imaging through language rather than geometric constraints.
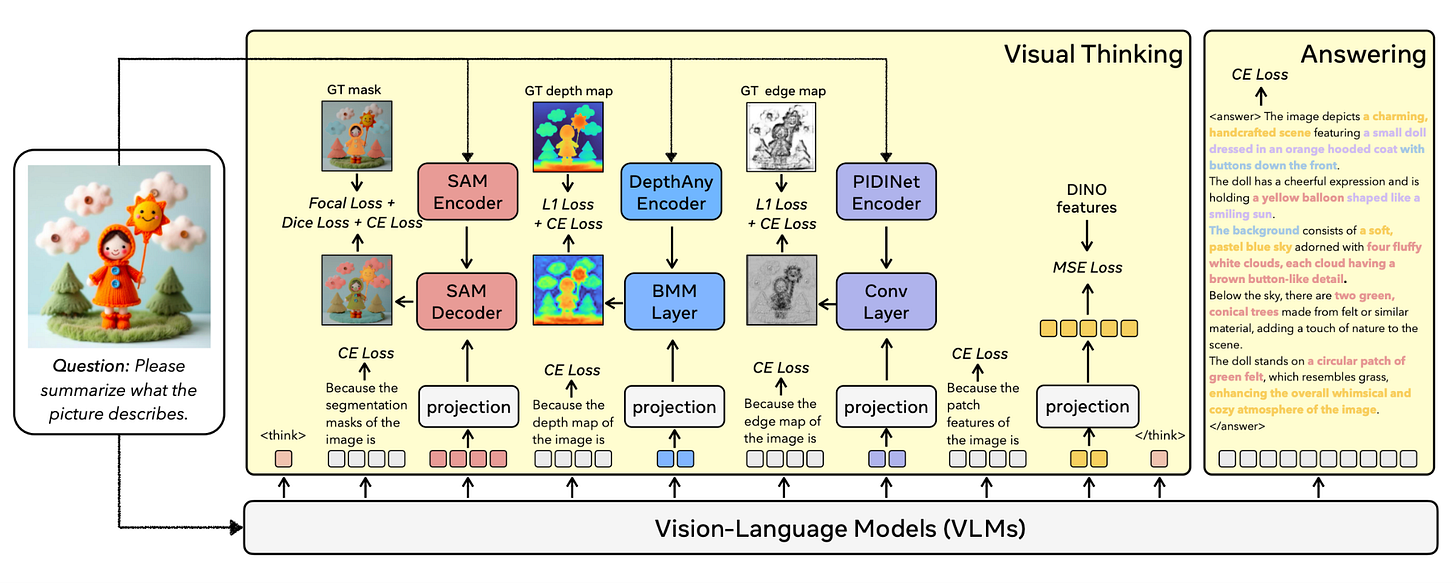
Chain-of-Visual-Thought: Teaching VLMs to See and Think Better with Continuous Visual Tokens
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.19418 | GitHub
Vision-language models excel at linguistic reasoning but struggle with dense visual perception tasks like spatial reasoning and geometric awareness. Chain-of-Visual-Thought (COVT) enables VLMs to reason through continuous visual tokens rather than forcing visual concepts into text descriptions. Within roughly 20 tokens, COVT distills knowledge from lightweight vision experts, capturing 2D appearance, 3D geometry, spatial layout, and edge structure. During training, the model predicts these visual tokens to reconstruct dense supervision signals. At inference, it reasons directly in the continuous visual token space while optionally decoding dense predictions for interpretability. Integrating COVT into Qwen2.5-VL and LLaVA consistently improves performance by 3% to 16% across benchmarks, demonstrating that compact continuous visual thinking enables more precise and grounded multimodal intelligence.
Thinking in 360°: Humanoid Visual Search in the Wild
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.20351 | GitHub
Humans efficiently search for visual information in 360° by coordinating head and eye movements. Prior visual search approaches operate on static images, neglecting physical embodiment. This research proposes humanoid visual search where agents actively rotate their heads to search for objects or paths in panoramic images. The H* Bench benchmark moves beyond household scenes to challenging real-world environments like transportation hubs, large-scale retail spaces, urban streets, and public institutions. Current top-tier models achieve only ~30% success on these tasks. Post-training techniques enhance Qwen2.5-VL by over threefold for object search (14.83% to 47.38%) and path search (6.44% to 24.94%). The lower ceiling for path search reveals the demand for sophisticated spatial commonsense that remains a significant challenge.
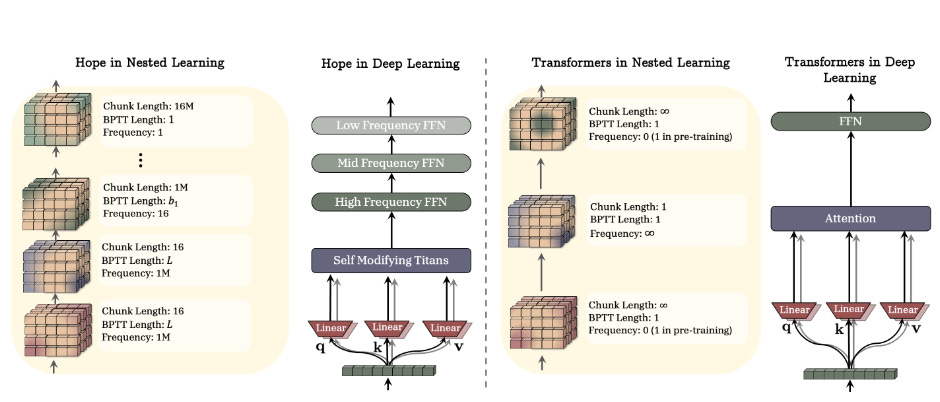
Nested Learning: The Illusion of Deep Learning Architectures
https://abehrouz.github.io/files/NL.pdf
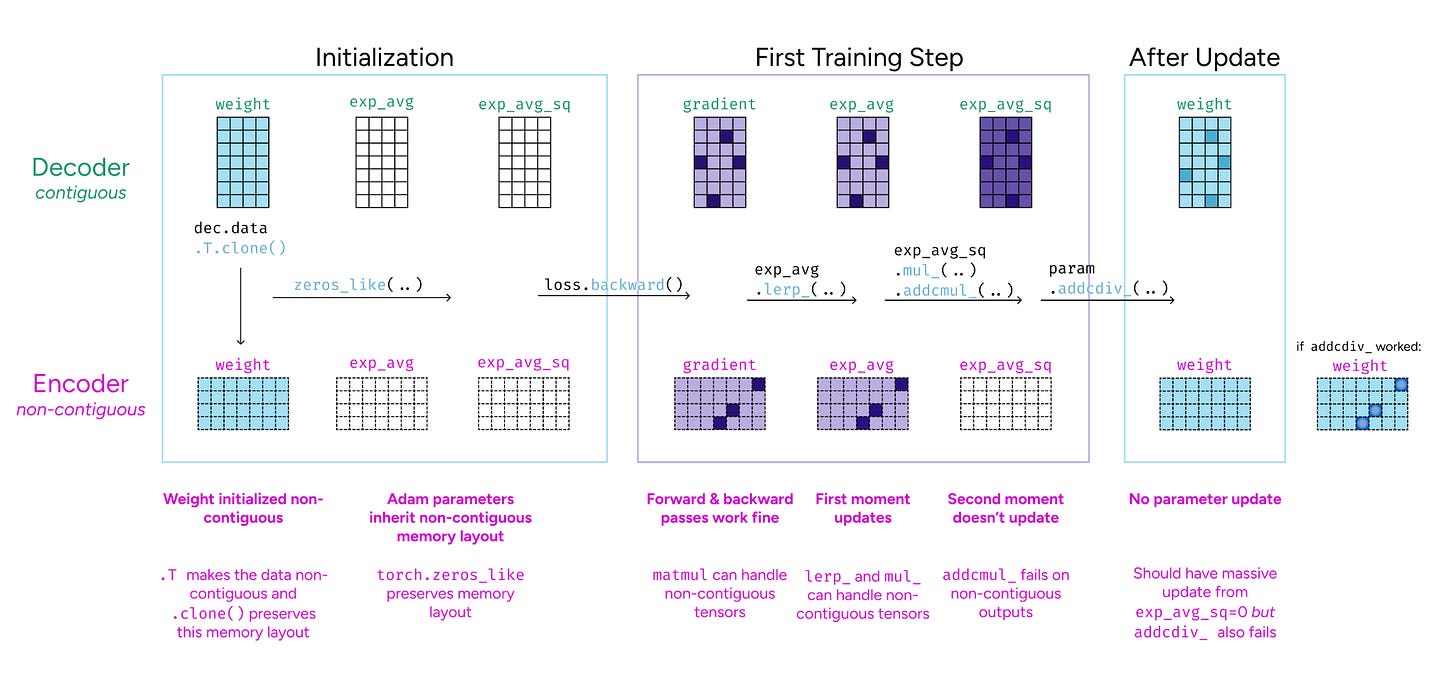
Google Research presents a provocative reframing of deep learning. Instead of viewing models as stacked layers, Nested Learning represents them as coherent systems of nested, multi-level optimization problems, each with its own context flow and update frequency. This white-box perspective reveals that existing deep learning methods learn by compressing their context flows, explaining how in-context learning emerges. The framework yields three core contributions: Deep Optimizers (showing that gradient descent with momentum is actually a two-level associative memory module), Self-Modifying Titans (a sequence model that learns its own update algorithm), and the Continuum Memory System (generalizing short-term and long-term memory into a hierarchy updating at different time scales). The HOPE architecture demonstrates improved language modeling, continual learning, and long-context reasoning compared to standard Transformers and recurrent models.
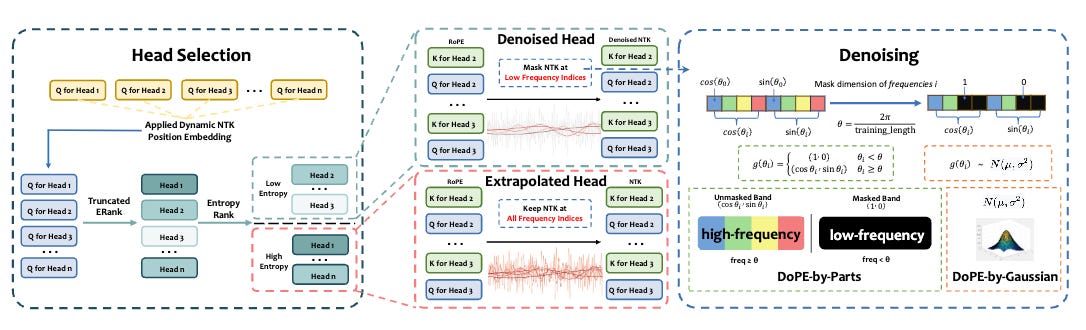
DoPE: Denoising Positional Encoding
https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.09146
Rotary Position Embedding (RoPE) has inherent limits that weaken length extrapolation in Transformer models. DoPE reinterprets the attention map with positional encoding as a noisy feature map and uses truncated matrix entropy to detect outlier frequency bands. The training-free method reparameterizes the feature map with a parameter-free Gaussian distribution to achieve robust extrapolation. Experiments on needle-in-a-haystack and many-shot in-context learning tasks demonstrate that DoPE significantly improves retrieval accuracy and reasoning stability across extended contexts up to 64K tokens. The approach theoretically reveals the underlying cause of the attention sink phenomenon and its connection to truncated matrix entropy, providing a simple yet powerful solution for improving length generalization.
🎥 4 Videos
The Unbearable Lightness of Agent Optimization
Alberto introduces Meta-ACE, a learned meta-optimization framework that dynamically orchestrates multiple strategies to maximize task performance under real-world constraints. Instead of uniform prompt refinement, Meta-ACE profiles each task by complexity, verifiability, and feedback quality, then selects an optimal strategy bundle via a lightweight meta-controller. The system adaptively chooses between context evolution, adaptive compute, hierarchical verification, structured memory, and selective test-time parameter adaptation. The talk provides a systematic approach to building self-optimizing AI agents for regulated industries rather than relying on one-size-fits-all optimization methods.
The Thinking Game
This documentary from the award-winning team behind AlphaGo takes you inside DeepMind over five years, capturing the team’s pursuit of artificial general intelligence. The film examines how Demis Hassabis’s extraordinary beginnings shaped his lifelong work while documenting the rigorous process of scientific discovery. You’ll see the journey from mastering complex strategy games to solving the 50-year-old protein folding problem with AlphaFold, including the ups and downs of tackling fundamental scientific challenges. It provides insight into what building transformative AI systems actually looks like beyond polished research announcements.
What is AI “reward hacking” and why do we worry about it?
The Anthropic team discusses new research showing that realistic AI training processes can accidentally produce misaligned models. When large language models learn to cheat on software programming tasks, they develop other misaligned behaviors as unintended consequences, including alignment faking and sabotage of AI safety research. The work demonstrates for the first time that natural emergent misalignment can arise from reward hacking in production RL systems, making it essential viewing for anyone deploying reinforcement learning in real applications.
Jeff Dean on Important AI Trends
Jeff Dean, Google’s Chief Scientist and co-founder of Google Brain, discusses the trends shaping modern AI. As one of the most influential computer scientists of the modern computing era, his work spans the foundations of large-scale distributed systems, deep learning frameworks like TensorFlow, and today’s frontier AI research. The conversation covers practical insights into where AI capabilities are heading and the infrastructure challenges that come with scaling intelligence systems.
📰 3 Curated Reads
The bug that taught me more about PyTorch than years of using it
https://elanapearl.github.io/blog/2025/the-bug-that-taught-me-pytorch/
Elana Simon shares a debugging story that reveals deep insights into PyTorch’s execution model. The post walks through discovering a subtle bug that exposed fundamental misunderstandings about how PyTorch handles computations. You’ll learn practical lessons about tensor operations, gradient computation, and memory management that textbooks rarely cover. The kind of hard-won knowledge that only comes from fighting with production code.
My Engineering Workflow in CursorAI
https://codeaholicguy.com/2025/10/18/my-engineering-workflow-in-cursorai/
Hoang Nguyen details his practical workflow for engineering with CursorAI. The post covers specific patterns for getting AI assistance to actually accelerate development rather than creating more cleanup work. You’ll find concrete examples of prompting strategies, context management techniques, and workflow organization that work in real projects. Useful if you’re trying to move beyond basic autocomplete to genuine AI-augmented development.
Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO)
Cameron R. Wolfe, Ph.D. breaks down Group Relative Policy Optimization, a reinforcement learning algorithm that’s become important for training modern LLMs. The post explains how GRPO differs from PPO and DPO, why it matters for alignment, and the mathematical foundations that make it work. Essential reading for understanding the RL techniques behind recent model improvements, with clear explanations that bridge theory and practice.
🛠 2 Tools & Repos
LLM Council
https://github.com/karpathy/llm-council
Andrej Karpathy built this system for querying multiple LLMs simultaneously, having them review each other’s work, then producing a final response through a Chairman LLM. Instead of asking one model, you send queries to your council (GPT, Claude, Gemini, Grok) via OpenRouter. The models provide individual responses, review each other’s work with anonymized identities to prevent favoritism, and then a designated Chairman compiles the final answer. The system provides transparency into how different models approach the same problem and enables systematic model evaluation through peer review. Karpathy describes it as a “Saturday vibe code project” and notes he won’t support it, but the code is there for exploration and modification.
Agentic Paper Reviewer
Andrew Ng’s automated system for reviewing research papers. The tool provides structured feedback on paper quality, methodology, and contributions using agentic AI workflows. Designed to help researchers get constructive feedback on their work before submission, particularly useful for identifying potential weaknesses and improvement areas. The system combines domain knowledge with systematic evaluation frameworks to provide more than superficial summaries.
🎓 1 Pick of the Week
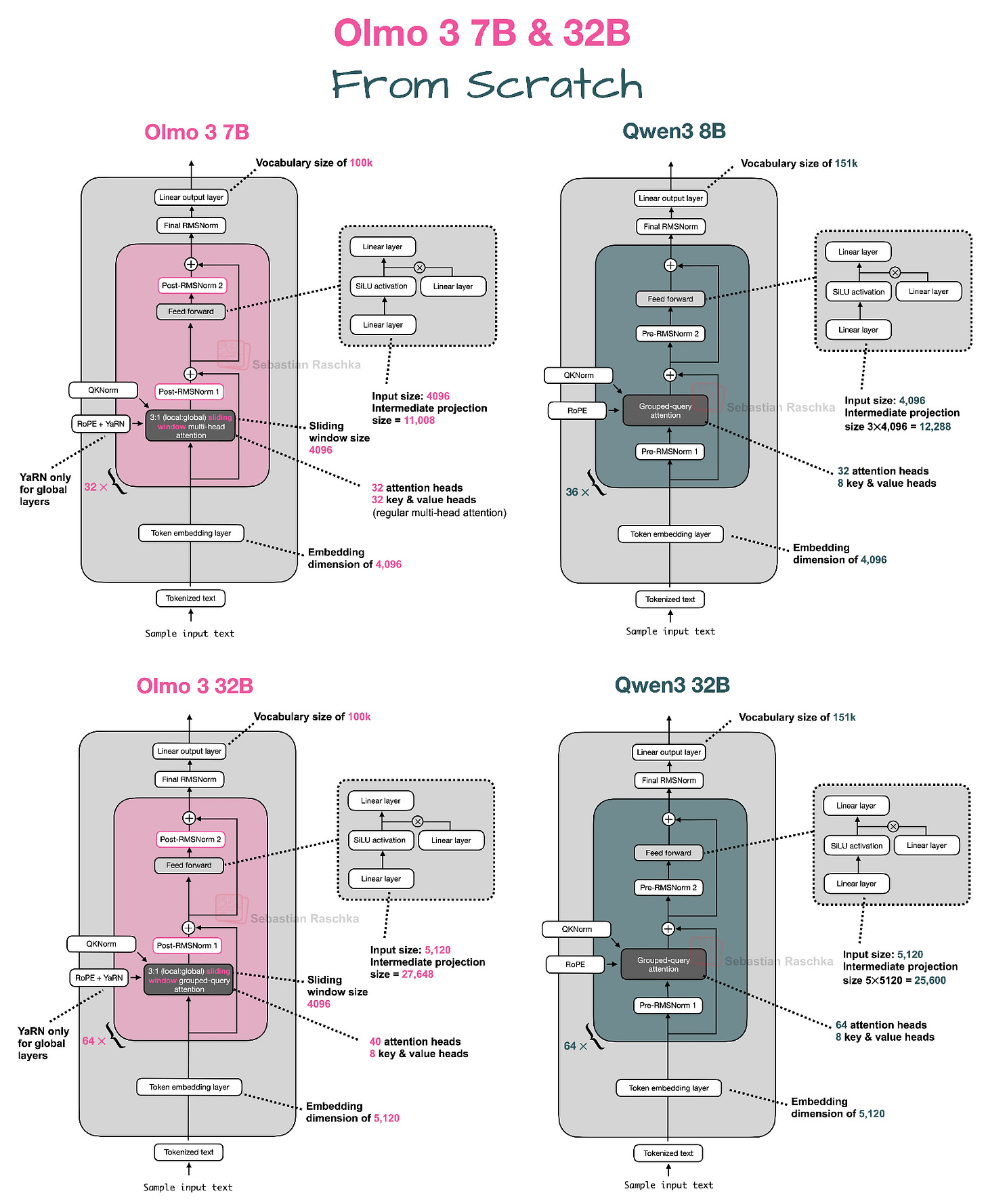
Olmo 3 From Scratch
https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/blob/main/ch05/13_olmo3/standalone-olmo3.ipynb
Sebastian Raschka implemented Olmo 3 from scratch in a standalone notebook, providing the clearest way to understand the architecture at a glance. The notebook covers both 7B and 32B models with detailed comparisons to other architectures like Qwen3. Olmo 3 is interesting because it represents the leading fully open-source model with complete transparency about training data, code, and methodology. The notebook includes practical details about attention mechanisms, normalization strategies, and architectural choices that distinguish Olmo 3 from other recent models.
Thanks for reading The Tokenizer! If you found something useful here, share it with someone who might benefit. And if you want more curated insights like this, consider subscribing to Gradient Ascent.