NVIDIA Fixes Multi-Reward RL Collapse, Video Agents Lose Their Train of Thought, and LLM Benchmarks That Judge Themselves - 📚 The Tokenizer Edition #14
This week's most valuable AI resources
Hey there! NVIDIA identified a normalization issue in multi-reward RL where distinct reward combinations collapse into identical training signals. Video agents show consistent failures in maintaining focus through long retrieval chains. Someone built a framework to systematically evaluate benchmark quality. Also, new research questions whether the weight decay equilibrium we’ve accepted is optimal.
New here?
The Tokenizer is my resource-focused newsletter edition where I curate the best papers, videos, articles, tools, and learning resources from across the AI landscape. Consider it your weekly dose of everything you need to stay ahead in machine learning.
TL;DR
What caught my attention this week:
• 📄 Papers: NVIDIA’s fix for multi-reward RL signal collapse, video agents that drift off-task during web research, learnable multipliers escaping weight decay traps, RL-as-a-service infrastructure, and meta-benchmarks judging benchmark quality
• 🎥 Videos: Claude Agent SDK workshop with real-world integrations, why context stuffing isn’t memory, Codex fundamentals, and spec-driven AI development
• 📰 Reads: OpenAI’s framework for AI behavior governance, performance optimization principles that actually matter, and what LLM coding workflows look like in 2026
• 🛠 Tools: Simon Willison’s definitive 2025 LLM retrospective and production-ready Claude Code templates
• 🎓 Learning: Comprehensive modern AI course from foundations through deployment
Quick Plug: I’m running an ML and Generative AI System Design workshop with Packt.
We’ll cover the core design principles for building solid AI products: making systems reliable, measuring what matters, and designing architectures that work in production.
Use code FLASH40 for 40% off:
What topics/problems would you most want covered in a system design workshop? Drop a comment or DM me.
📄 5 Papers
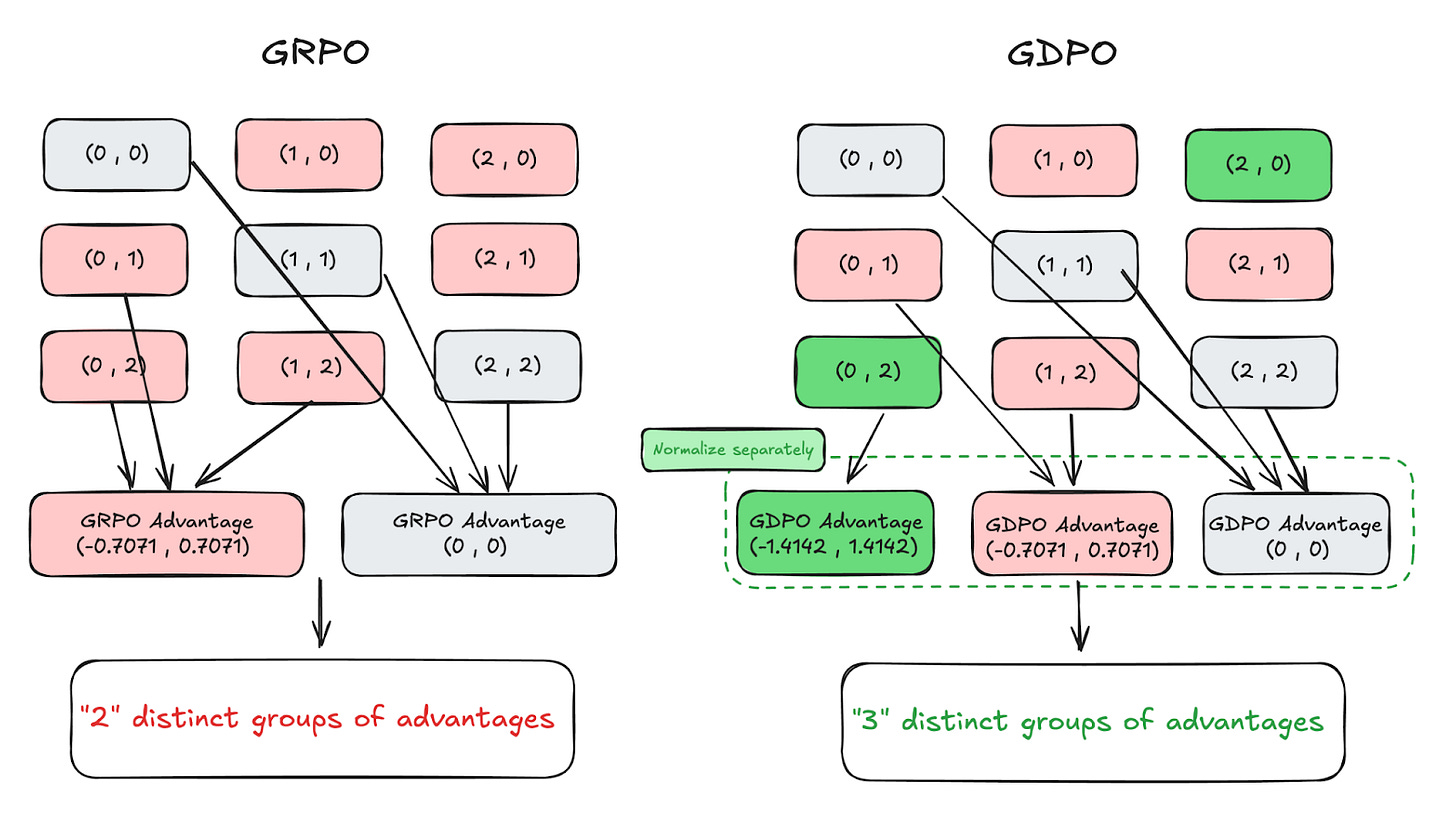
GDPO: Group reward-Decoupled Normalization Policy Optimization for Multi-reward RL Optimization
https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.05242 | Github
Multi-reward RL has a normalization problem. When GRPO normalizes the sum of distinct rewards, different reward combinations can collapse into identical advantage values. NVIDIA’s GDPO addresses this by normalizing each reward independently before aggregating them, preserving the relative differences between reward combinations. Testing on tool calling, math reasoning, and code generation shows consistent improvements. On AIME, training DeepSeek-R1-1.5B with GDPO yields 6.3% higher accuracy compared to GRPO while maintaining shorter response lengths. The method works as a drop-in replacement in verl and TRL frameworks.
Watching, Reasoning, and Searching: A Video Deep Research Benchmark on Open Web for Agentic Video Reasoning
https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.06943 | Github
VideoDR tests whether video agents can extract visual anchors from multiple frames, retrieve information from the open web, and combine evidence from both sources. The benchmark requires cross-frame visual extraction, interactive web retrieval, and multi-hop reasoning. Results show agentic approaches don’t consistently outperform workflow-based methods. The advantage appears when models maintain their initial video anchors throughout long retrieval chains. The evaluation across both Workflow and Agentic paradigms identifies goal drift and long-horizon consistency as the primary failure modes. The benchmark includes 100 video-question-answer triples across six semantic domains with annotation designed to prevent single-source solutions.
Learnable Multipliers: Freeing the Scale of Language Model Matrix Layers
https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.04890 | Github
Weight decay and stochastic gradient noise create an equilibrium that determines weight matrix norms through optimization hyperparameters rather than data. This work introduces learnable multipliers to test whether this equilibrium is optimal. Scalar multipliers attached to weight matrices show the equilibrium norm is suboptimal, with learned scales adapting to data and improving performance. Per-row and per-column multipliers extend this by freeing individual dimension scales. The approach generalizes muP multipliers with more expressivity, outperforms well-tuned muP baselines, and shows improvements with both Adam and Muon optimizers. Applied in Falcon-H1 pretraining with consistent downstream performance gains.
OpenTinker: Separating Concerns in Agentic Reinforcement Learning
https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.07376 | Github
OpenTinker provides RL infrastructure that separates environment specification from execution and resource management. Users define agents, environments, and interaction protocols while the system handles rollout generation, training, and scheduling through a managed runtime. The architecture supports both LoRA-based and full-parameter RL across shared cluster resources. A centralized scheduler manages multi-tenant workloads, allowing multiple users to run training jobs on shared infrastructure. The design extends to multi-agent training through an agent protocol coordinator that manages interaction order and synchronization within the environment abstraction.
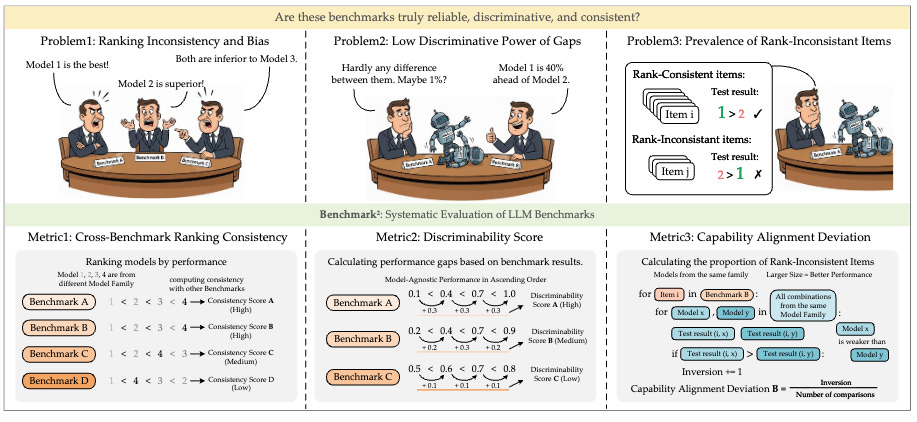
Benchmark^2: Systematic Evaluation of LLM Benchmarks
https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03986
This work introduces a framework for evaluating benchmark quality through three metrics: Cross-Benchmark Ranking Consistency (alignment with peer benchmark rankings), Discriminability Score (ability to differentiate between models), and Capability Alignment Deviation (whether stronger models within a family perform better). Testing across 15 benchmarks spanning mathematics, reasoning, and knowledge domains with 11 LLMs from four families reveals significant quality variations among existing benchmarks. The analysis shows that selective benchmark construction based on these metrics can achieve comparable evaluation performance with substantially reduced test sets.
🎥 4 Videos
Claude Agent SDK [Full Workshop]
Anthropic’s technical team walks through their Agent SDK and Response API. The workshop covers chain-of-thought tool calling patterns, the interface for defining agent behaviors, and production deployment considerations. Includes integration examples from Coinbase and Box demonstrating how the SDK works in real implementations.
Stuffing Context is not Memory, Updating Weights is
This talk examines the distinction between context windows and model memory. The discussion covers why adding information to context differs from updating model weights, with implications for system design. Relevant if you’re building systems that rely on context windows and need to understand their limitations.
Getting started with Codex
A practical introduction to Codex covering setup, integration patterns, and common workflows. Focuses on core functionality needed to evaluate whether Codex fits specific use cases.
Spec-Driven Development: Sharpening your AI toolbox
This talk covers how specification-driven development applies to AI systems. The approach involves defining clear specifications upfront and using them to guide development and validation, helping teams move from prototypes to production systems with more predictable behavior.
📰 3 Curated Reads
How should AI systems behave, and who should decide?
https://openai.com/index/how-should-ai-systems-behave/
Old but gold. OpenAI’s piece on frameworks for determining AI system behavior and who should influence those decisions. Covers the tension between universal standards and context-specific behavior with deployment examples. Addresses how to balance different stakeholder perspectives when defining appropriate AI behavior across varied use cases.
Performance Hints
https://abseil.io/fast/hints.html#performance-hints
Jeff Dean and Sanjay Ghemawat share some incredible insights on performance optimization, covering measurement methodology, common pitfalls, and when optimization matters. Examines the relationship between code clarity and performance, with principles that apply across frameworks and languages.
My LLM coding workflow going into 2026
Google’s Addy Osmani shares a practitioner’s account of using LLM-assisted coding in daily work. Covers specific tools, workflow patterns, where AI assistance provides value, and where it introduces friction. Focuses on practical integration with traditional development practices.
🛠 2 Tools & Repos
Simon Willison 2025 Review
https://simonwillison.net/2025/Dec/31/the-year-in-llms/
Simon Willison’s year-end retrospective connecting technical developments in LLMs to practical applications. The analysis identifies trends and developments from 2025 with context on their significance beyond benchmark performance. Useful for understanding how the field evolved over the year.
Claude Code Templates
https://github.com/davila7/claude-code-templates
Ready-to-use templates for Claude Code workflows across React, Vue, Django, FastAPI, and other frameworks. Each template includes CLAUDE.md configurations and setup patterns that work in practice. Reduces setup time when starting new projects.
🎓 1 Pick of the Week
CMU’s Modern AI Course
CMU’s free course covering AI from foundations through deployment starts on Jan 26th for folks online and not in the classroom. The curriculum includes core concepts, training methodologies, and practical implementation. It appears to balance mathematical foundations with hands-on projects. Structured for both newcomers building foundational knowledge and practitioners working on specific topics.
Thanks for reading The Tokenizer! If you found something useful here, share it with someone who might benefit. And if you want more curated insights like this, consider subscribing to Gradient Ascent.






Solid curation this week. The GDPO normalization fix is particuarly interesting - been wondering why multi-reward setups kept converging to similar behaviors despite different reward weights. The learnable multipliers paper challenging weight decay equilibrium is intriguing too, makes you question assumptions we've all just accepted. Gonna check out the VideoDR benchmark, that goal drift issue sounds familar from agent work I've done.